CVE-2025-55182 (React2Shell)
Critical RCE in React Server Components Under Active Exploitation
Critical RCE in React Server Components Under Active Exploitation

"Illustrated developer uncovering React2Shell vulnerability in React framework code, featuring dual displays with security alerts and neon hacker aesthetic"
Photo by Perplexity Labs
Feel free to send us a message with your thoughts, or learn more about us!
On January 13, 2026, Node.js released security patches for 8 vulnerabilities (3 HIGH, 4 MEDIUM, 1 LOW) affecting all active release lines. This post breaks down each CVE, explains who is affected, and provides actionable remediation guidance.
A multi-part series on building production-ready developer platforms: implementing CSP, rate limiting, INP optimization, analytics, and comprehensive security features.
Implement event-driven architecture with Inngest for instant API responses, automatic retries, and production-grade background processing. Real code from a live portfolio.
Today we witnessed defense in depth working exactly as intended. Within hours of CVE-2025-55182 being disclosed, a critical remote code execution vulnerability in React Server Components, we received alerts from two different sources:
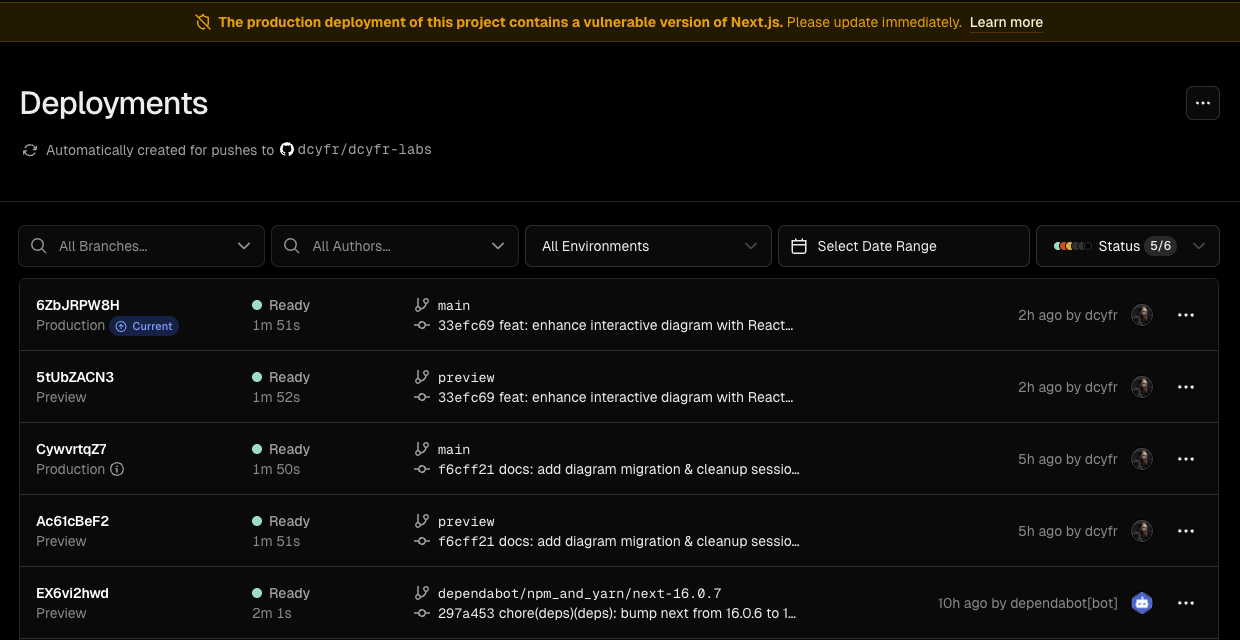
This is what modern security infrastructure looks like: multiple layers working in concert. Vercel’s WAF provided immediate protection before we could even review the PR, while Dependabot delivered the actual patch for permanent remediation.
In this post, we’ll break down what CVE-2025-55182 is, why it matters, how these layered defenses protected our app, and what you should do to secure your own projects.
Your development teams need immediate support to upgrade. React2Shell poses the same threat level as Log4Shell with confirmed botnet integration and nation-state exploitation. Budget emergency patching cycles and engage your security team.
CVE-2025-55182, also known as “React2Shell” in the security community, is a critical-severity vulnerability affecting . Under certain conditions, specially crafted requests can lead to unintended on the server.
Technical Details:
react-server-dom-parcel, react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-turbopack)| Package | Affected Versions | Fixed Versions | Recommended (Jan 2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| React | 19.0.0 - 19.2.0 | 19.0.1, 19.1.2, 19.2.1+ | 19.2.3+ (all 4 CVEs fixed) |
| Next.js | ≥14.3.0-canary.77, all 15.x, all 16.x | 15.0.5+, 16.0.7+ | 16.0.10+ (latest hardened) |
Other affected frameworks: Vite with RSC, Parcel, React Router (RSC), RedwoodSDK, Waku
Quick Version Check:
npm ls next react # or check package.jsonUse Vercel's automated fix tool for fastest remediation: npx fix-react2shell-next. If self-hosting, deploy available WAF rules (Cloudflare, AWS WAF) while you test upgrades. Monitor for compromise using the detection patterns below.
Following React2Shell’s disclosure, researchers discovered three additional vulnerabilities4:
| CVE | Severity | Impact | Patched In |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-55182 | CRITICAL | Remote Code Execution | React 19.0.1+ |
| CVE-2025-55183 | MEDIUM | Source code exposure | React 19.2.2+ |
| CVE-2025-55184 | HIGH | Denial of Service | React 19.2.2+ (incomplete) |
| CVE-2025-67779 | HIGH | DoS (bypass of CVE-2025-55184) | React 19.2.3+ |
Critical: CVE-2025-55184’s original fix was incomplete4. Upgrade directly to React 19.2.3+ to address all four vulnerabilities in one update8.
Attack Chain Context: Exploitation is fully automated, progressing from scanner identification to payload deployment in under 10 seconds. Attackers use PowerShell arithmetic validation (powershell -c "40138*41979"), encoded payloads, AMSI bypasses, then deploy cryptocurrency miners, backdoors, and credential harvesters.
Here’s what makes this disclosure interesting from a DevSecOps perspective: Vercel’s platform detected and mitigated this vulnerability before Dependabot could even create a PR.
The disclosure and exploitation unfolded rapidly:
Both systems worked, but with different roles and limitations:
As of December 8, 2025:
Vercel coordinated with the React team pre-disclosure, deployed WAF rules automatically to all projects, and continuously improved protections as bypass variants emerged. They released automated fix tooling (npx fix-react2shell-next) and began blocking new vulnerable deployments.
“We have created new WAF rules to address this vulnerability and deployed them to Vercel WAF that will automatically and at no cost protect all projects hosted on Vercel.” — Jimour Lai, Vercel Security Engineer
Important WAF Limitations: Vercel acknowledges that “WAF rules are one layer of defense but can never guarantee 100% coverage.” As new exploit variants emerged (evidenced by payload variations observed on December 8), Vercel identified and patched WAF bypasses, but upgrading remains the only complete fix.
CISA Recognition: The addition of CVE-2025-55182 to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities list on December 5 signals that this is now considered a priority threat by federal agencies, underscoring the urgency of remediation.
This means that while the WAF provided valuable defense-in-depth, our production deployment wasn’t truly secure until we merged the upgrade. The WAF bought us time and reduced risk, but it wasn’t a substitute for patching.
Vercel also worked with the React team to provide recommendations to major WAF and CDN providers. This collaborative approach helps protect the broader ecosystem, not just Vercel customers.
In an unprecedented security initiative, Vercel launched a $1 million bug bounty program specifically targeting WAF bypass techniques:
Program Results:
Dual-Layer Defense Architecture:
Vercel deployed a two-layer protection system:
Layer 1: Seawall WAF
Layer 2: Runtime Mitigation (First Public Disclosure)
This runtime layer provided visibility into actual WAF bypass attempts in production, allowing Vercel to state “with high confidence that the WAF was extraordinarily effective”—because they had ground truth data from the second layer.
Automated Remediation Tools:
One month after disclosure, React2Shell has achieved unprecedented exploitation scale:
Volume Metrics:
Infrastructure Analysis:
Five China-nexus threat clusters have been specifically attributed (AWS + Google Threat Intelligence)5:
Advanced Tactics:
Security researchers have identified seven sophisticated malware families deployed specifically through CVE-2025-551826:
Professional-Grade Tooling:
PeerBlight Linux Backdoor6
Even with cloud provider WAF protections, you must upgrade. WAF rules provide interim protection but are not a permanent fix.
Implement detection for PowerShell Event ID 4104 AMSI bypasses, encoded commands, and unusual RSC POST patterns. Scan for .env credential theft, systemd persistence, and cryptocurrency mining. Five China-nexus APT groups are actively exploiting this vulnerability.
For Next.js Projects:
# Option 1: Use Vercel's automated fix tool (recommended)
npx fix-react2shell-next
# Option 2: Manual upgrade to latest patched versions
npm install next@latest react@latest react-dom@latest
# Option 3: Specify exact versions (January 2026 recommendations)
npm install next@16.0.10 react@19.2.3 react-dom@19.2.3Verify Your Upgrade:
npm ls next react react-domFor Other RSC Frameworks: Check framework documentation and ensure React 19.2.3+ (addresses all 4 ).
$1 Million Bug Bounty Program Results:
Dual-Layer Defense Architecture:
Layer 1: Seawall WAF
Layer 2: Runtime Mitigation (First Public Disclosure)
Automated Remediation Tools:
Automatically Deployed (No Action Required):
AWSManagedRulesKnownBadInputsRuleSet v1.24+Available for Deployment:
Open Source Scanners:
github.com/assetnote/react2shell-scannerEnterprise Security Platforms:
Signs of Active Exploitation:
Network Indicators:
_prefix, _chunks, _formData patternsSystem Indicators:
-enc/-EncodedCommand flagsamsiInitFailed, AmsiUtils)For Vercel Customers:
For Other Hosting:
Defense-in-Depth (NOT Complete Protection):
Critical Reality Check: Active botnet exploitation means constant probing. Every hour of delay increases risk exponentially.
Security researchers are now comparing React2Shell to Log4Shell in terms of long-term impact and exploitation trajectory7:
Wiz Research has provided comprehensive statistics on React2Shell’s impact10:
Vulnerability Exposure:
Similar Exploitation Velocity:
Ubiquitous Framework Creates Massive Attack Surface:
Long-Tail Exploitation Expected:
Unlike typical vulnerabilities that see exploitation decline after initial waves, React2Shell exhibits characteristics of permanent infrastructure risk:
Organizations should treat React2Shell as a persistent threat requiring ongoing vigilance, not a one-time patch event. The vulnerability’s integration into criminal infrastructure, nation-state operations, and automated exploitation frameworks ensures it will remain a significant risk factor for years to come.
React Server Components represent a significant architectural shift. They blur the line between client and server code, which creates new attack surfaces that didn’t exist in traditional client-side React.
This vulnerability is a reminder that:
Server-side code needs server-side security thinking. RSC isn’t “just React”, it’s React running in a privileged environment.
Framework-level protections matter. Vercel’s ability to deploy WAF rules across their platform demonstrates the value of managed infrastructure.
The disclosure process is evolving. Coordinated disclosure with platform providers can protect users faster than traditional CVE → Dependabot → CI workflows.
npx fix-react2shell-next automates the upgrade processThis incident highlights several important lessons for DevSecOps teams:
Credit: This vulnerability was responsibly disclosed by Lachlan Davidson. Thanks to Jimour Lai, Luba Kravchenko, and Andy Riancho at Vercel for the coordinated response.
GreyNoise. “CVE-2025-55182 (React2Shell) Opportunistic Exploitation In The Wild.” GreyNoise Intelligence, January 2026. greynoise.io; CyberSecurityNews. “Hackers Launched 8.1 Million Attack Sessions to React2Shell.” CyberSecurityNews, January 2026. cybersecuritynews.com
npx fix-react2shell-next automated fix toolPost-Exploitation Artifacts:
Credential Harvesting Targets:
# Check these files for unauthorized access
.env*, ~/.ssh/*, ~/.aws/credentials, ~/.docker/config.json
~/.git-credentials, ~/.bash_history, /etc/shadow, /etc/passwdPersistence Mechanisms:
The vulnerability affects React Server Components (RSC) broadly, including Server Components, Server Actions, and any RSC-based rendering pipeline. If you’re using Next.js App Router (13+), you’re using RSC and potentially affected.
SiteGuarding. “Critical React Server Components Vulnerability Exposes Over 644,000 Domains.” SiteGuarding Security Blog, January 2026. siteguarding.com; CybersecurityDive. “React Server Components crisis escalates.” CybersecurityDive, January 2026. cybersecuritydive.com
CISA. “Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog.” Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, December 2025. cisa.gov; Gopher Security. “CISA’s KEV Catalog Grows by 1,484 Vulnerabilities in 2025.” Gopher Security, December 2025. gopher.security
React Team. “Denial of Service and Source Code Exposure in React Server Components.” React Blog, December 2025. react.dev; The Hacker News. “New React RSC Vulnerabilities Enable DoS and Source Code Exposure.” The Hacker News, December 2025. thehackernews.com
AWS Security. “China-nexus cyber threat groups rapidly exploit React2Shell vulnerability.” AWS Security Blog, December 2025. aws.amazon.com; Google Cloud. “Multiple Threat Actors Exploit React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182).” Google Cloud Threat Intelligence, December 2025. cloud.google.com; Rescana. “CVE-2025-55182 React2Shell: Chinese APT Groups Exploit Critical React Server Components Vulnerability.” Rescana, December 2025. rescana.com
Huntress. “PeerBlight Linux Backdoor Exploits React2Shell CVE-2025-55182.” Huntress Blog, January 2026. huntress.com; The Hacker News. “React2Shell Vulnerability Actively Exploited to Deploy Linux Malware.” The Hacker News, December 2025. thehackernews.com; GBHackers. “PeerBlight Linux Malware Abuses React2Shell for Proxy Tunneling.” GBHackers, January 2026. gbhackers.com
Bitdefender. “Technical Advisory: React2Shell Critical Unauthenticated RCE in React.” Bitdefender Blog, December 2025. bitdefender.com; Talent500. “React2Shell: The Critical React Vulnerability Reshaping Frontend Security.” Talent500 Blog, December 2025. talent500.com
Mondoo. “How to Fix Critical React and Next.js Vulnerabilities.” Mondoo Blog, December 2025. mondoo.com
AWS Security. “China-nexus cyber threat groups rapidly exploit React2Shell vulnerability.” AWS Security Blog, December 2025. aws.amazon.com
Wiz Research. “React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182): Critical React Vulnerability.” Wiz Blog, December 2025. wiz.io
CyberScoop. “Inside Vercel’s sleep-deprived race to contain React2Shell.” CyberScoop, December 2025. cyberscoop.com; The Hacker News. “React2Shell Exploitation Delivers Crypto Miners and New Malware.” The Hacker News, December 2025. thehackernews.com
The Hacker News. “Critical React2Shell Flaw Added to CISA KEV After Confirmed Active Exploitation.” The Hacker News, December 2025. thehackernews.com
Cloudflare. “React2Shell and related RSC vulnerabilities threat brief.” Cloudflare Blog, December 2025. blog.cloudflare.com
Microsoft Security. “Defending against the CVE-2025-55182 (React2Shell) vulnerability.” Microsoft Security Blog, December 2025. microsoft.com
Dynatrace. “React2Shell CVE-2025-55182: What it is and what to do.” Dynatrace Blog, December 2025. dynatrace.com
JFrog. “React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182): Detection & Mitigation Guide.” JFrog Blog, December 2025. jfrog.com